FILE: <ch122-htm> GENERAL INDEX
[Navigate to MAIN MENU ]
[
|
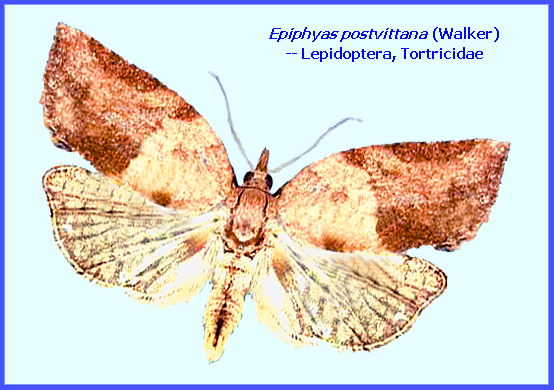
LIGHT BROWN APPLE MOTH Epiphyas postvittana (Walker),
Lepidoptera, Tortricidae (Contacts) -----
CLICK on Photo to enlarge & search for Subject Matter with Ctrl/F. GO TO ALL: Bio-Control Cases
Identification is made through an examination of the reproductive
system. The moth’s description,
habits and potential control are detailed by Varela et al (2008). Control
in 2008 has focused on eradication efforts by government agencies. However, the widespread nature of the
pest, and its tenacious foothold in numerous countries worldwide that have
diverse climates does not bode well for the permanency of such an expensive,
and upsetting to other components of the ecosystem procedure. Paul & Austen (2006) in Australia have
reported the existence of parasitic insects attacking the moth. Further explorations on native host plants
in more remote, nonagricultural areas of that continent as well as
neighboring Indonesia might yield additional candidates for biological
control. Furthermore, the native home
may not always be the best place to search for effective natural enemies, as
was shown with the importation of the South American Goniozus legneri
Gordh to control carob moth, Ectomyelois ceratoniae (Zeller),
an Old World species. <ch-121.htm> REFERENCES: [Additional references may be found at: MELVYL
Library ] Bailey, P.,
G. Baker, G. Caon. 1996. Field efficacy and persistence of Bacillus
thuringiensis var kurstaki against Epiphyas postvittana
(Walker) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in relation to larval behaviour on
grapevine leaves. Aust. J. Entomol.
35: 297-302. Bellas, T.
E., Bartell, R. J., Hill, A.
1983. Identification of two
components of the sex pheromone of the moth, Epiphyas postvittana
(Lepidoptera, Tortricidae). J. Chem.
Ecol. 9: 503-12. Bradley, J. D. 1973. Epiphyas
postvittana (Walker). IN: British Tortricoid Moths. Cochylidae and Tortricidae: Tortricinae. Ray Soc., London, p. 126-7. Brockerhoff, E. G., H. Jactel, Leckie, A. C., Suckling, D. M. 2002. Species composition
and abundance of leafrollers in a Canterbury pine plantation. New Zealand Plant Protect. 55: 85-9. Buchanan, G. A. 1977.
The seasonal abundance and control of light brown apple moth, Epiphyas
postvittana (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), on grapevines in
Victoria. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 28: 125-32. Buchanan, G. A., Stirrat, S. C., Madge, D. G. 1991. Integrated control of light brown apple moth,
Epiphyas postvittana (Walker),
in vineyards. Wine Ind. J.
6: 220-2. California
Dept. of Food & Agriculture.
2007a. Light brown apple moth
host list. www.cdfa.ca.gov/phpps/PDEP/target_pest_disease_profiles/LBAM_HostList.pdf. 6 p. California
Dept. of Food & Agriculture.
2007b. Light brown apple moth
project: Advisories, PSA No. 12-2007. www.cdfa.ca.gov/phpps/pdep/lbam/advisories.html. 4 p. California
Dept. of Food & Agriculture.
2007c. Light brown apple moth
situation reports. www.cdfa.ca.gov/phpps/PDEP/lbam/situationreports.html. 4 p. California
Dept. of Food & Agriculture.
2007d. Plant Quarantine
Manual: Light Brown Apple Moth State
Interior Quarantine. http://pi.cdfa.ca.gov/pqm/manual/pdf/419.pdf. 19 p. Canadian
Food Inspection Agency. 2007. Plant protection (phytosanitary) import
requirements to prevent the entry of Epiphyas postvittana (Walker) (light
brown apple moth). www.inspection.gc.ca/english/plaveg/protect/dir/d-07-03e.shtml#12c. Charles, J.
G., Walker, J. T. S., White, V.
1996. Leafroller phenology and
parasitism in Hawkes Bay, New Zealand, canefruit gardens, New Zeal, J. Crop Hort. Sci. 24: 123-31. Danthanarayana,
W. 1975. The bionomics, distribution and host range of the light brown
apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Walk.) (Tortricidae). Aust. J. Zool. 23: 419-37. Danthanarayana, W. 1976. Environmentally
cued size variation in the light-brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana
(Walker.) (Tortricidae), and its adaptive value in dispersal. Oecologia 26: 121-32. Danthanarayana, W. 1983.
Population ecology of the light-brown apple moth, Epiphyas
postvittana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae).
J. Anim. Ecol. 52: 1-33. Danthanarayana, W., Gu, H., Ashley, H. 1995. Population growth potential of Epiphyas
postvittana, the light brown apple moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in
relation to diet, temperature and climate.
Aust. J. Zool. 43: 381-94. Dugdale, J. S., D. Gleeson, Clunie, L. H., Holder,
P. W. 2005. A diagnostic guide to Tortricidae encountered in field surveys
and quarantine inspections in New Zealand:
Morphological and molecular characters. Ministry of Agric. & Forest., Wellington, NZ. 161 p. Geier, P. W., Briese, D. T. 1980.
The light-brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Walker): 4.
Studies on population dynamics and injuriousness to apples in the
Australian Capital Territory. Aust.
J. Ecol. 5: 63-93. Mo, J.,
Glover, M., Munro, S., Beattie, G. A. C.
2006. Evaluation of mating
disruption for control of lightbrown apple moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in
citrus. J. Econ.
Entomol. 99: 421-6. Paull, C. Austin, A. D. 2006.
The hymenopteran parasitoids of light brown apple moth, Epiphyas
postvittana (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in Australia. Aust. J. Entomol. 45: 142-56. Rogers, D.
J., Walker, J. T. S., Moen, I. C. et al. 2003. Understorey influence on leafroller populations in
Hawke’s Bay organic apple orchards.
New Zeal. Plant Protect 56:
168-73. Suckling,
D. M., Brunner, J. F., Burnip, G. M., Walker, J. T. S. 1994.
Dispersal of Epiphyas postvittana (Walker) and Planotortrix octo
Dugdale (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) at a Canterbury, New Zealand orchard. New Zeal. J. Crop. Hort. Sci. 22: 225-34. Suckling,
D. M., Burnip, G. M., Walker, J. T. S. et al. 1998.
Abundance of leafrollers and their parasitoids on selected host plants
in New Zealand, New Zeal. J. Crop. Hort. Sci. 26: 193-203. Suckling,
D. M., Clearwater, J. R. 1990. Small scale trials of mating disruption of
Epiphyas postvittana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Environ. Entomol. 19: 1702-9. U. S. Dept.
of Agriculture Animal & Plant Health Inspection Service. 2007a.
Federal domestic quarantine order Epiphyas postvittana (light
brown apple moth) DA-2007-42. www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/plant_pest_info/iba_moth/downloads/federalorder-11-20-07.pdf. 5 p. U. S. Dept.
of Agriculture Animal & Plant Health Inspection Service. 2007b.
Light Brown Apple Moth (LBAM) Regulatory Protocol. APHIS Plant Protection and
Quarantine. www.aphis.usda.gov/plant_health/olant_pest_info/lba_moth/downloads/lbam-regulatoryprotocol.pdf. 2 p. Varela, L. G., M. W. Johnson, L. Strand, C. A. Wilen & C.
Pickel. 2008. Calif. Agric 62(2): 57-61. Wearing, C. H., Thomas, W. P., Dugdale, J. S., Danthanarayana,
W. 1991. Tortricid pests of pome and stonefruits. Australian and New Zealand species. IN:
Tortricid Pests: Their
Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control.
World Crop Pests, Vol. 5. Elsevier:
Amsterdam. P. 453-72. Zimmerman, E. C. 1978. Insects of Hawaii: Microlepidoptera. Honolulu:
Univ. Pr. Hawaii. 1,923 p. |